Artificial intelligence and machine learning technologies can improve the collection and analysis of social media data and the effectiveness of social media intelligence.
In today's digital age, the number of people accessing the internet is increasing every day. Most of these people have one or more social media accounts. According to Statista, in January 2024, the number of internet users worldwide was 5.35 billion; 5.04 billion are active on different social media platforms.
People now rely on social media platforms to socialize, engage with news content, leverage them as a communication medium instead of cellar networks (using WhatsApp and Facebook Messenger) and share their leisure and work activities.
For companies, social media platforms provide a cost-effective solution to reach customers, receive feedback, build brand awareness and promote products and services.
The vast volume of data available on social media platforms has become a valuable resource for OSINT (open source intelligence) gatherers. In fact, gathering open source information specifically from social media has spawned an acronym of its own: SOCMINT.
In this article, I will discuss how OSINT gatherers can leverage the latest technological advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) technologies to collect data on a mass scale, gain powerful insights about social media content and enhance the effectiveness of social media analysis.
Key techniques for using AI-powered tools in social media analysis
AI and ML technologies have introduced significant advances in gathering, processing and analyzing digital data. For instance, OSINT gatherers can leverage these technologies to:
- Gather open source data from a plethora of publicly accessible sources
- Facilitate dealing with different types of languages
- Extracting valuable information from the gathered data and categorizing them according to different criteria
In the following sections, I will detail how we can use AI and ML technologies for SOCMINT investigations:
Natural language processing (NLP)
NLP algorithms can automate the process of scraping data from social media platforms on a mass scale in addition to facilitating extracting the following information:
- Textual data including tweets, Facebook posts, comments and replies, Reddit threads and subreddits, Instagram posts, etc.
- The sentiment expressed in the gathered social media posts, classifying them according to different criteria (e.g., themes discussed in social media conversations)
- Named entities from large volumes of unstructured text, whether they are people, businesses, products, services, locations or events names; for instance, a company can track the mention of its brand, named product or service across different social media platforms
- Languages used in social media posts, thus removing posts written in a specific language; this dramatically reduces the volume of data that OSINT gatherers must analyze
- Specific keywords from social media posts based on the search requirements of the OSINT investigators
- Large “chunks” of text in posts and replies, summarizing such content and returning the essence of the conversation
- Users’ emotions when writing social media posts or other text content, such as anger, love and hate; for example, there are tools to perform sentiment analysis on text, such as Free Sentiment Analyzer by Dr. Daniel Soper and Watson Natural Language Understanding from IBM (see Figure 1)
Figure 1 - The IBM Watson Natural Language Understanding Text Analysis can be used to extract different types of information from provided text or URLs
Identify automated accounts
AI and ML technologies can be used to identify automated bots that are widely used on social media platforms to spread disinformation. For instance, we can perform anomaly detection on social media posts by training ML models on the normal known behavior of a group of social media users. Any deviation in their future behaviors (e.g., posting frequency, language complexity, active hours, excessive use of hashtags/URLs and how they interact with other users/pages across the platform) can be recognized as bot activity and flagged for human inspection.
ML can also be leveraged to analyze how different accounts communicate with each other across the social media platform. For example, accounts run by bots commonly interact with other bot accounts to orchestrate coordinated activities, such as disseminating fake news or posting links to malicious websites. These signals could reveal suspicious bot accounts by monitoring such account interactions, examining when they were created, their date/time activity patterns and each account's follower/following metrics.
There are many online tools for spotting bot accounts on social media platforms; here are some examples:
- Bot Sentinel: This is a free platform to detect and track suspicious Twitter bot accounts. Bot Sentinel uses ML and AI to study Twitter accounts and classify them based on different criteria, such as whether they are trustworthy or not. It then stores those accounts in a database and tracks them daily (see Figure 2 of the Bot Sentinel Dashboard).
- Botometer X: Use this tool to calculate the likelihood an account is automated (a bot) on the Twitter (X) platform. This tool is currently in archival mode, and its results are calculated based on the historical data gathered before May 31, 2023; however, we can still use it to check Twitter accounts before that period.
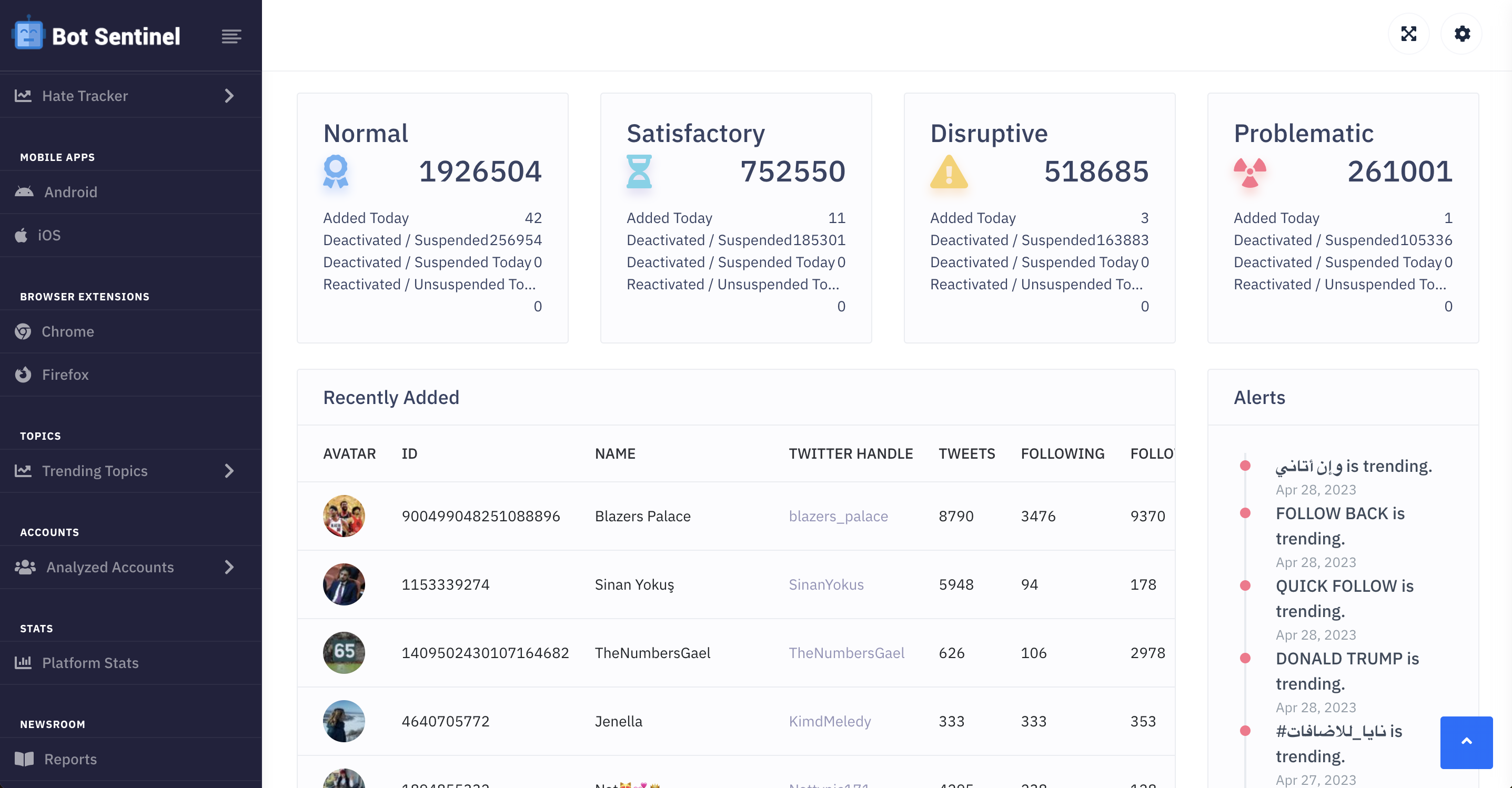
Figure 2 - Bot Sentinel Dashboard
Image and video analysis
After the public release of ChatGPT and other generative AI tools, the ability to create fake content increased significantly at almost no cost. Social media platforms have become full of content created using AI tools, such as images and videos, in addition to text content. OSINT gatherers need to find a way to distinguish these contents to avoid including them in their search results and consequently provide inaccurate intelligence reports.
AI and ML can scan social media posts to distinguish images and videos created using AI tools from those created by humans through various techniques:
Pattern detection
AI-generated images and videos may have unique patterns (e.g., inconsistent texture areas, noise patterns, compression artifacts) that trained ML models can detect.
AI tool fingerprint
AI tools leave a unique fingerprint when creating images and videos. Examples of such fingerprints include:
- Subtle checkerboard-like patterns that especially appear in smooth gradients or textures of AI-generated images
- Over-smoothing or blurriness, mainly when complex texture backgrounds are used
- Repeated patterns — some AI tools may replicate a specific object in the generated image more than once
Trained ML models can be used to detect such content automatically. If you want to use a tool for performing manual detection of a few objects like images, you can use any of the following tools:
- AI or Not: used to detect both image and audio contents
- Content at Scale
- AI Image Detector
- SynthID from Google
Of course, OSINT gatherers can utilize other techniques to spot AI-generated images, such as reverse image search (Bing, Google) and inspecting image/video metadata.
Some tools to inspect image metadata:
- ExifTool
- Exif Pilot
- Azure AI Vision — an AI tool powered by Microsoft that can extract a wide variety of visual features from your images
See the Silo for Research exif viewer in action >
Network and relationships analysis
AI and ML technologies can significantly help OSINT gatherers analyze networks and relationships on social media platforms via the following methods:
- Discover potential connections on social media platforms, identify influencing users and uncover hidden relationships
- Extract users' relationships automatically, such as family members, friends and work colleagues, by analyzing users' posts, comments, likes, shares and other interactions
- Group users according to their interests; for example, by analyzing thousands of Facebook posts, we can group users based on their interest in a specific subject or area based on their interactions about a particular topic or event
In this article, we saw how AI can be used in various scenarios to aid OSINT gatherers in exploiting the massive volume of public data available across different social media platforms.
Remember to stay secure and anonymous when gathering intelligence. Protect your identity and the intent of your investigation with a purpose-built digital investigation platform like Silo for Research.
Tags OSINT research Social media

